Essential VS Training Specific Supplementation
n1 training
Essential supplementation includes the things that we consider necessary to support optimal overall health and support regular biological function regardless of the training stimulus. There is no doubt that supplementation can have an important role in today’s world with the increased environmental stresses and decreased natural food quality relative to decades past. They can increase recovery, performance, and quality of life. However, supplements are still a support, rather than a replacement, for a high quality diet and properly designed training program.
Essential Supplements
We believe there are certain supplements that are beneficial for most people simply for supporting biological function and overall health regardless of the training stimuli. The ideal dosage may vary, but here are what we consider the “essentials” in no particular order.
- Multi-Vitamin
- Powdered Greens
- Fish Oil (EPA/DHA)
- Taurine
- Vitamin D3 + K
- Chelated Magnesium (Glycinate is the most commonly used)
- Electrolytes (Synerplex by KT Solutions is our preferred formula)
- Activated B Vitamins (Pure Encapsulations B-Complex)
To view some of the products we recommend for these, visit the Supplements page and view the N1 Essentials category in the Nutri-Dyn store.
Training Supplements
As we get in to supplementation for training, things can get very specific as we start dialing in to a stimuli-based approach as well as considering individual differences. If you are interested in learning more about the details of each, consider taking the Nutrition & Program Design for Trainability course.
In this article we’ll be focusing on the basics that can apply within the three phases of training or for certain goals. There are several others that can be used conditionally based on the training and goal.
Many of the essentials also play a role in peri-workout nutrition and can be varied based on the type of training. For example, an activated B-complex can be a good option pre-workout to support energy production and mental focus while taurine can be a staple addition post-workout to help with calming the nervous system, facilitating electrolyte balance, and aiding in glucose sensitivity.
Keep in mind that ALL of these have an “it depends” factor that influence if or when you might apply them.
BCAAs can be a useful addition intra-workout to support the liver during metabolically demanding workouts or when glycogen stores might be low. Most often this would be utilized in a hypertrophy or metabolic phase.
Glutamine can play several important roles when utilized around training. If carbohydrates are low, large doses of glutamine can aid in glycogen replenishment in the absence of glucose (1,2).
It also helps the kidneys buffer acid. This can be helpful in phases where there is a lot of lactate or metabolic waste being produced during training. 5-10g intra-workout is usually sufficient for this aspect and it does not detract from the metabolic benefits of lactic acid production during training.
Glycine has a useful function as a growth hormone secretagogue. This means that it supports and enhances the production of GH (3,4). For this use, glycine can be used after a metabolic workout to promote the body’s natural GH production. However, this also should be in an instance with little to no carbs. Otherwise an elevation of insulin can inhibit the production of growth hormone after the session.
Tyrosine can be beneficial pre-workout in all three phases phases to improve focus and neurological drive. It has the benefits of both increasing the neurotransmitter dopamine as well as playing a role in thyroid hormone production , which can be helpful for a fat loss goal. The amount of this amino will depend on the type of training session as some stimuli will be better suited to a lower amount of dopamine than others. In addition, too much dopamine can increase irritability and make it difficult to focus during the session.
Acetyl-L-Carnitine is useful for mental focus and amplifying the effects of nutrients that increase the neurotransmitters dopamine and acetylcholine. This form is primarily used because it more easily crosses the blood-brain barrier. It is not used with the intent of increasing fat burning directly by enhancing transport of fatty acids into the mitochondria like most people associate with carnitine supplementation.
To learn more about pre-workout nootropics, check out THIS ARTICLE.
For more pre-workout supplement considerations, check out THIS ARTICLE.
These are just some of the basics training specific possibilities with many more depending on individual needs and goals. The Nutrition & Program Design for Trainability course does in depth on pre, intra, and post-workout nutrition and supplementation for each phase of training if you want to learn more. It is also part of N1 Online Coaching if you prefer to have all the recommendations laid out for you.
ATP Labs
Use code N1TEN for 10% off your entire order
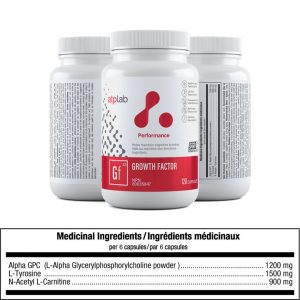
Growth Factor
Pre-Workout with Tyrosine, Alpha GPC, and Acetyl-L-Carnitine
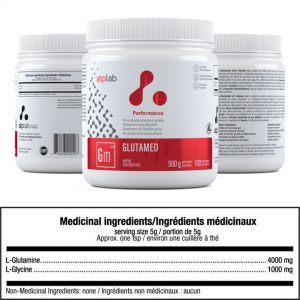
GlutaMed
Glutamine plus glycine
SynerMag
Magnesium glycinate with taurine and B6 to increase absorption
Nutri-Dyn
Get 10% off your entire order when you set up your account HERE.
Check out the N1 Essentials category on the Supplements page for the following:
Fruits & Greens: The best tasting and highest quality powdered greens we’ve ever found
Phyto-Multi: Multivitamin with phytonutrients
Omega Pure: Highest quality fish oil in capsule or liquid form
Vitamin D3 + K2: 5,000 or 10,000 IU with vitamin K2 for increased absorption
Essential supplementation includes the things that we consider necessary to support optimal overall health and support regular biological function regardless of the training stimulus. There is no doubt that supplementation can have an important role in today’s world with the increased environmental stresses and decreased natural food quality relative to decades past. They can increase recovery, performance, and quality of life. However, supplements are still a support, rather than a replacement, for a high quality diet and properly designed training program.
Essentials for Health
We believe there are certain supplements that are beneficial for most people simply for supporting biological function and overall health regardless of the training stimuli. The ideal dosage may vary, but here are what we consider the “essentials” in no particular order.
- Multi-Vitamin
- Powdered Greens
- Fish Oil (EPA/DHA)
- Taurine
- Vitamin D3 + K
- Chelated Magnesium (Glycinate is the most commonly used)
- Electrolytes (Synerplex by KT Solutions is our preferred formula)
- Activated B Vitamins (Pure Encapsulations B-Complex)
To view some of the products we recommend for these, visit the Supplements page and view the N1 Essentials category in the Nutri-Dyn store.
Training Specific
As we get in to supplementation for training, things can get very specific as we start dialing in to a stimuli-based approach as well as considering individual differences. If you are interested in learning more about the details of each, consider taking the Nutrition & Program Design for Trainability course.
In this article we’ll be focusing on the basics that can apply within the three phases of training or for certain goals. There are several others that can be used conditionally based on the training and goal.
Many of the essentials also play a role in peri-workout nutrition and can be varied based on the type of training. For example, an activated B-complex can be a good option pre-workout to support energy production and mental focus while taurine can be a staple addition post-workout to help with calming the nervous system, facilitating electrolyte balance, and aiding in glucose sensitivity.
Keep in mind that ALL of these have an “it depends” factor that influence if or when you might apply them.
BCAAs can be a useful addition intra-workout to support the liver during metabolically demanding workouts or when glycogen stores might be low. Most often this would be utilized in a hypertrophy or metabolic phase.
Glutamine can play several important roles when utilized around training. If carbohydrates are low, large doses of glutamine can aid in glycogen replenishment in the absence of glucose (1,2).
It also helps the kidneys buffer acid. This can be helpful in phases where there is a lot of lactate or metabolic waste being produced during training. 5-10g intra-workout is usually sufficient for this aspect and it does not detract from the metabolic benefits of lactic acid production during training.
Glycine has a useful function as a growth hormone secretagogue. This means that it supports and enhances the production of GH (3,4). For this use, glycine can be used after a metabolic workout to promote the body’s natural GH production. However, this also should be in an instance with little to no carbs. Otherwise an elevation of insulin can inhibit the production of growth hormone after the session.
Tyrosine can be beneficial pre-workout in all three phases phases to improve focus and neurological drive. It has the benefits of both increasing the neurotransmitter dopamine as well as playing a role in thyroid hormone production , which can be helpful for a fat loss goal. The amount of this amino will depend on the type of training session as some stimuli will be better suited to a lower amount of dopamine than others. In addition, too much dopamine can increase irritability and make it difficult to focus during the session.
Acetyl-L-Carnitine is useful for mental focus and amplifying the effects of nutrients that increase the neurotransmitters dopamine and acetylcholine. This form is primarily used because it more easily crosses the blood-brain barrier. It is not used with the intent of increasing fat burning directly by enhancing transport of fatty acids into the mitochondria like most people associate with carnitine supplementation.
To learn more about pre-workout nootropics, check out THIS ARTICLE.
For more pre-workout supplement considerations, check out THIS ARTICLE.
These are just some of the basics training specific possibilities with many more depending on individual needs and goals. The Nutrition & Program Design for Trainability course does in depth on pre, intra, and post-workout nutrition and supplementation for each phase of training if you want to learn more. It is also part of N1 Online Coaching if you prefer to have all the recommendations laid out for you.
Recommended Sources
ATP Labs
Use code N1TEN for 10% off your entire order
Growth Factor
Pre-Workout with Tyrosine, Alpha GPC, and Acetyl-L-Carnitine
GlutaMed
Glutamine plus glycine
SynerMag
Magnesium glycinate with taurine and B6 to increase absorption
Nutri-Dyn
Get 10% off your entire order when you set up your account HERE.
Check out the N1 Essentials category on the Supplements page for the following:
Fruits & Greens: The best tasting and highest quality powdered greens we’ve ever found
Essential Multi: Multivitamin with phytonutrients
Omega Pure: Highest quality fish oil in capsule or liquid form
Vitamin D3 + K2: 5,000 or 10,000 IU with vitamin K2 for increased absorption
Have a Question for Us?
Please Log In to Submit Your Question
BCAAs – Anabolic & Anti-Catabolic
articleBody Composition FREE Hypertrophy Nutrition SupplementationOmega-3s For Health & Body Composition
articleBody Composition FREE Health and Longevity Nutrition Supplementation
Popular Pages
Learn & Train With Us
Add N1 Training to your Homescreen!

Please log in to access the menu.