Digestion 101
n1 training
A great quote by my mentor Charles Poliquin is that, “it doesn’t matter what you ingest, it matters what you can assimilate.” What this refers to is that eating healthy and taking all the supplements in the world doesn’t make much of a difference if you are not able to properly digest them. In this article we are going to discuss the role of the stomach in digestion.
The stomach basically has two major functions for digesting your food. It has a mechanical and an endo-chemical process. The endo-chemical part is the production of gastric juices that start to break down your food, kill microbes, and stimulate the later parts of digestion. The mechanical process is basically a way of swishing around your food in the stomach to break it up and expose all the food to the gastric juices.
Let’s start at the beginning. When you eat, you are using almost all your senses to prepare your digestive system for the food in which it is about to receive. The smells, the taste, receptors on the mouth, tongue, and throat, the mechanical motion of chewing all work to signal your body that food is coming. Experiments have even shown that auditory signals like a dinner bell can begin the digestive process. The final message is actually a stretch reflex of the stomach which stimulates the medulla oblongata. The medulla then signals your body to release the hormone gastrin.
Gastrin is the hormone that tells your stomach to start releasing it’s gastric juices. The muscular walls of the stomach contract vigorously to mix food with gastric juice, producing a mixture called chyme. The majority of people with digestive issues have a problem with the gastric juices their stomach is creating. Most people are familiar with heartburn or acid reflux, which is sometimes caused by overactive production of acid, but can also be caused by the sphincter between the stomach and the esophagus malfunctioning allowing the stomach’s normal healthy acids to leak up into the esophagus.
Another cause of the heartburn or GERD sensations is alkaline reflux. Most people don’t realize that not having enough acidity in the stomach can cause the same and even worse problems than having too much. Also treating acid reflux and heartburn by buffering or stopping acid production can lead to long term health problems. Taking these kinds of medications rather than healing the stomach and restoring proper function can result in the loss of digestive function.
Gastric juices are made of 3 main components.
- A mucus that protects the stomach lining from the acid and digestive enzymes in the stomach.
- Pepsinogen, which is converted to pepsin, which digests proteins. Pepsinogen production is stimulated by the presence of gastrin in the blood.
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl) converts pepsinogen to pepsin which breaks down proteins to peptides. HCl maintains a pH in the stomach of approximately 2.0. It also dissolves food and kills microorganisms.
A growing problem is impaired HCl production. It’s estimated that about 40-50% of the US population suffers from low stomach acid levels. Without enough HCl, pepsinogen can not be converted into pepsin, which means that you can not break down the protein in your food. Don’t be fooled into thinking it will be broken down later in the intestinal tract either. The intestines are more involved in the final stages of digestion and more importantly absorption. If you don’t break down the large compounds of food like protein and fiber in the stomach, you will not be getting the valuable nutrients from your diet. Cruciferous vegetables are known for their estrogen-detoxification properties through the production of Diindolylmethane from Indole-3-Carbinol, but this extraction cannot occur without an adequate amount of HCl.
Not producing enough HCl also makes you more prone to bacterial and fungal overgrowth and parasites. These can further hamper your digestion and have numerous other negative health impacts on your body. Low HCl also puts you at greater risk for food poisoning and infections. Low HCl production is also associated with increased risk in gastric cancer and many diseases related to nutrient deficiencies. For instance, low B12 is associated with Alzheimer’s but many of these cases are because they don’t produce enough stomach acid to absorb the B12.
Signs you are not producing enough HCl
- Belching or gas within one hour of a meal
- Bloating and fullness shortly after eating
- Loss of taste for meat
- Nausea after taking supplements
- Brittle fingernails
- Undigested food in stool
- Foul-smelling stools
- Stomach pain
- Bad breath
- Loss of appetite
- Estrogen buildup
- Acne rosacea
- Depression
Stomach acid is also important for signaling later processes in digestion to digest fats and carbohydrates. If you need to increase the levels of HCL to properly digest your food, tablets can be consumed with meals. Betaine HCL is a commonly available form which can be found in most health food stores or online retailers. Start on the low range of dosing at about 250-500mg. If the symptoms are not reduced or eliminated you may increase the dose with your next meal by about 250mg. Once you feel a slight warming sensation in your stomach, you have reached your effective dose.
A great quote by my mentor Charles Poliquin is that, “it doesn’t matter what you ingest, it matters what you can assimilate.” What this refers to is that eating healthy and taking all the supplements in the world doesn’t make much of a difference if you are not able to properly digest them. In this article we are going to discuss the role of the stomach in digestion.
The stomach basically has two major functions for digesting your food. It has a mechanical and an endo-chemical process. The endo-chemical part is the production of gastric juices that start to break down your food, kill microbes, and stimulate the later parts of digestion. The mechanical process is basically a way of swishing around your food in the stomach to break it up and expose all the food to the gastric juices.
The Process
Let’s start at the beginning. When you eat, you are using almost all your senses to prepare your digestive system for the food in which it is about to receive. The smells, the taste, receptors on the mouth, tongue, and throat, the mechanical motion of chewing all work to signal your body that food is coming. Experiments have even shown that auditory signals like a dinner bell can begin the digestive process. The final message is actually a stretch reflex of the stomach which stimulates the medulla oblongata. The medulla then signals your body to release the hormone gastrin.
Gastrin is the hormone that tells your stomach to start releasing it’s gastric juices. The muscular walls of the stomach contract vigorously to mix food with gastric juice, producing a mixture called chyme. The majority of people with digestive issues have a problem with the gastric juices their stomach is creating. Most people are familiar with heartburn or acid reflux, which is sometimes caused by overactive production of acid, but can also be caused by the sphincter between the stomach and the esophagus malfunctioning allowing the stomach’s normal healthy acids to leak up into the esophagus.
Another cause of the heartburn or GERD sensations is alkaline reflux. Most people don’t realize that not having enough acidity in the stomach can cause the same and even worse problems than having too much. Also treating acid reflux and heartburn by buffering or stopping acid production can lead to long term health problems. Taking these kinds of medications rather than healing the stomach and restoring proper function can result in the loss of digestive function.
Gastric Fluid Composition
Gastric juices are made of 3 main components.
- A mucus that protects the stomach lining from the acid and digestive enzymes in the stomach.
- Pepsinogen, which is converted to pepsin, which digests proteins. Pepsinogen production is stimulated by the presence of gastrin in the blood.
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl) converts pepsinogen to pepsin which breaks down proteins to peptides. HCl maintains a pH in the stomach of approximately 2.0. It also dissolves food and kills microorganisms.
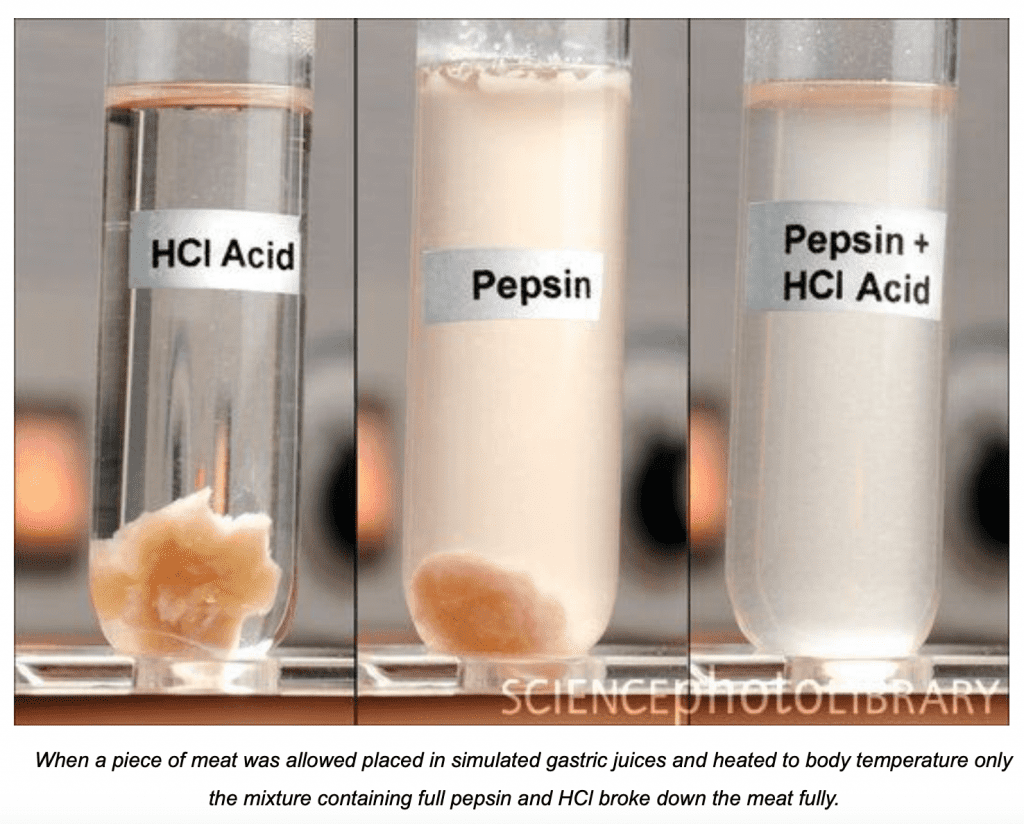
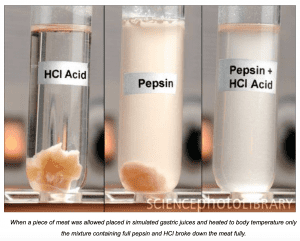
Low HCL Production
A growing problem is impaired HCl production. It’s estimated that about 40-50% of the US population suffers from low stomach acid levels. Without enough HCl, pepsinogen can not be converted into pepsin, which means that you can not break down the protein in your food. Don’t be fooled into thinking it will be broken down later in the intestinal tract either. The intestines are more involved in the final stages of digestion and more importantly absorption. If you don’t break down the large compounds of food like protein and fiber in the stomach, you will not be getting the valuable nutrients from your diet. Cruciferous vegetables are known for their estrogen-detoxification properties through the production of Diindolylmethane from Indole-3-Carbinol, but this extraction cannot occur without an adequate amount of HCl.
Not producing enough HCl also makes you more prone to bacterial and fungal overgrowth and parasites. These can further hamper your digestion and have numerous other negative health impacts on your body. Low HCl also puts you at greater risk for food poisoning and infections. Low HCl production is also associated with increased risk in gastric cancer and many diseases related to nutrient deficiencies. For instance, low B12 is associated with Alzheimer’s but many of these cases are because they don’t produce enough stomach acid to absorb the B12.
Signs you are not producing enough HCl
- Belching or gas within one hour of a meal
- Bloating and fullness shortly after eating
- Loss of taste for meat
- Nausea after taking supplements
- Brittle fingernails
- Undigested food in stool
- Foul-smelling stools
- Stomach pain
- Bad breath
- Loss of appetite
- Estrogen buildup
- Acne rosacea
- Depression
Stomach acid is also important for signaling later processes in digestion to digest fats and carbohydrates. If you need to increase the levels of HCL to properly digest your food, tablets can be consumed with meals. Betaine HCL is a commonly available form which can be found in most health food stores or online retailers. Start on the low range of dosing at about 250-500mg. If the symptoms are not reduced or eliminated you may increase the dose with your next meal by about 250mg. Once you feel a slight warming sensation in your stomach, you have reached your effective dose.
Have a Question for Us?
Please Log In to Submit Your Question
Is Sleep Affecting Your Insulin Sensitivity?
articleBody Composition Foundation FREE Health and Longevity
Popular Pages
Learn & Train With Us
Add N1 Training to your Homescreen!

Please log in to access the menu.